Birmingham opens Europe’s first pancreatic cancer mRNA vaccine trial
Researchers at BHP founding-members University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust (UHB) and the University of Birmingham have opened a trial to study how messenger RNA (mRNA) cancer vaccines may be used to prevent recurrence of pancreatic cancer. The Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham (QEHB) is the first hospital in Europe to recruit into such a trial.
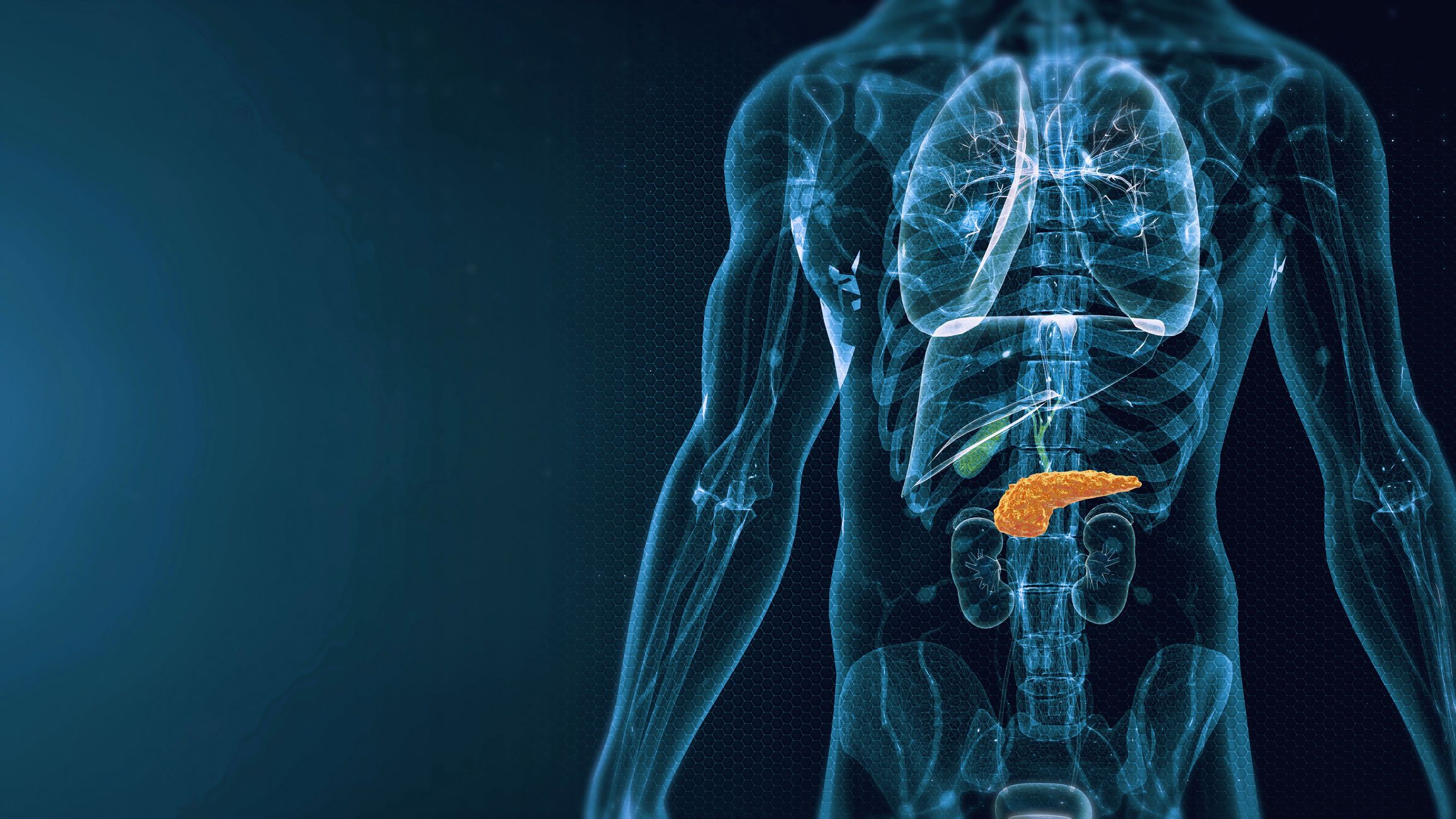
Pancreatic cancer is among the deadliest cancers globally, with a survival rate beyond 10 years of just 5% in England (2013-2017). It is often only when the cancer has reached an advanced stage that physical symptoms appear, at which point it becomes more difficult to treat.
The trial aims to recruit patients undergoing surgery to remove pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), an extremely aggressive disease that accounts for 90% of all pancreatic cancers.
Patients enrolled in the study will either receive an investigational cancer vaccine combined with chemotherapy (treatment group) or standard chemotherapy alone (control group).
In this investigational therapeutic cancer vaccine, mRNA is used to deliver the instructions for building several proteins (neoantigens) found in a person’s cancer. In doing so, the trial vaccine aims to train the immune system to recognise and attack the set of proteins (usually found on microscopic cancer cells) when it encounters it again.
Following surgery, samples of the patients’ tumour tissue and blood are sent to laboratories, to design and manufacture the investigational cancer vaccine. For the patients eligible for the trial, a mRNA-based cancer treatment is manufactured with mRNA specific to the proteins in that individual’s tumour.
This novel treatment approach is aimed at training the immune system to recognise and attack cancer cells, to potentially prevent cancer recurrence and increase the prospect of a patient being cured.
Dr Shivan Sivakumar, Principal Investigator of the trial, Associate Professor in Oncology at the University of Birmingham and Consultant Medical Oncologist at QEHB said: “We are incredibly proud that the Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham is the first site in Europe to enrol a patient to this investigational pancreatic cancer vaccine trial. This achievement highlights Birmingham’s leading role in advancing cancer treatment, offering new hope for patients battling one of the most challenging cancers we face today.
“We recently also became the first site in Europe to open an immunotherapy study in cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer), another deadly cancer. Birmingham is positioning itself to be a leading centre in Europe to test novel treatments for these hard-to-treat cancers and I find it humbling that patients in the Midlands have been able to enrol onto this trial, before anyone else in Europe.”
Professor Kiran Patel, Chief Medical Officer at UHB, which operates QEHB, added: “We are very fortunate to have exceptional infrastructure and world-class talent that positions us perfectly to lead in vital areas of cancer research.
“This trial showcases the expertise and dedication of our medical professionals, and the fantastic teams supporting them, who are at the leading edge of clinical research here in Birmingham.
“To be the first site to open in Europe, reaffirms our role as a national and international centre for cutting-edge oncology and highlights our commitment to improving patient outcomes through pioneering approaches.”
Jo Gray, Head of Research and Development Operations at UHB, said: “Through the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Wellcome Trust Clinical Research Facility (CRF), we are able to provide expert care to patients receiving experimental therapies. Birmingham is the first site outside of North America to open and to enrol a patient onto this complex, early phase trial, that addresses an important need to identify better post-surgery treatments for pancreatic cancer.”
Professor Neil Hanley, Head of the College of Medical and Dental Sciences at the University of Birmingham, said: “This work epitomises why the University of Birmingham and its tremendous partnership with UHB is delivering life-changing impacts.
“Whilst such approaches were being investigated before 2020, we now know the power of mRNA vaccines from the COVID-19 pandemic; to tilt those discoveries from a time of tremendous challenge towards a much-needed world of new cancer treatments is inspiring for all of us.
“Birmingham is the ideal place to open this trial, with one of the leading pancreatic cancer units in the UK and serving a super diverse population. The chemistry between the university and hospitals is clear. By working as one team under the banner of Birmingham Health Partners, we are delivering the kind of cutting-edge research leading to transformational clinical care that befits Birmingham as an innovative city at the forefront of health and life sciences.”
Dr Chris Macdonald, Head of Research at Pancreatic Cancer UK, said: “For too long we have had so few treatment options for people with pancreatic cancer. Surgery is currently the only potential cure and yet, tragically, in 75% of cases the cancer reoccurs within a year. Finally, there is hope on the horizon.
“We are absolutely delighted that Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham is the first site in Europe to enrol a patient to an individualised pancreatic cancer vaccine trial. We will be following the results with great interest, as the potential here cannot be understated. If this research proves successful, the vaccine could be a vital new weapon against the deadliest common cancer.”